Bitumen Emulsion
An emulsion can be defined as a dispersion of small droplets of one liquid in another. Bitumen emulsions generally belong to the oil-in-water type of emulsions where bitumen is dispersed in water with the aid of a small quantity of emulsifying agent. The agent stabilizes the bitumen particles under normal conditions of storage. Bitumen emulsions derive their main use in road construction and maintenance because of their safety, ease in handling and excellent adhesion properties.
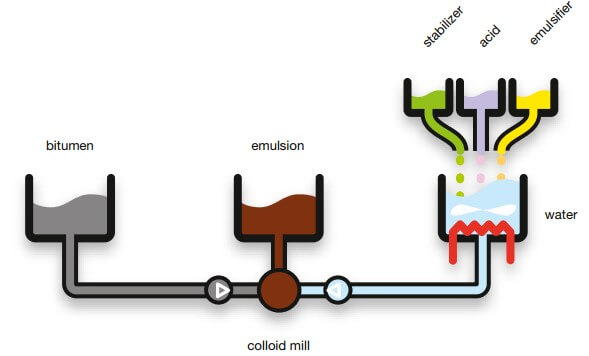
Bitumen emulsion production involves at least two process steps-water phase (soap) preparation and the actual emulsion production. The water phase is prepared in a tank into which heated water, emulsifier and other emulsion chemicals are metered and the solution properly mixed. In the emulsion production process the bitumen and the pre-made water phase are dosed to the colloid mill
here are two different ways to classify bitumen emulsion, as given below.
- Based on surface charge
- Based on setting time
BASED ON SURFACE CHARGE
Depending upon the type of surface charge, bitumen emulsions are primarily classified into the following two types.
- Anionic Bitumen Emulsion
- Cationic Bitumen Emulsion
In case of an anionic bitumen emulsion, bitumen particles are electro-negatively charged, whereas for cationic emulsions, bitumen particles are electro-positively charged.


The choice of bitumen emulsion (i.e. whether anionic or cationic) to be used depends upon the mineral composition of aggregate used for construction. In case of silica rich aggregates, the surface of the aggregates is electro-negatively charged. Therefore, a cationic emulsion should be used. This will help better spreading and binding of bitumen with aggregates.
BASED ON SETTING TIME
When bitumen emulsions are applied on aggregates, water starts to evaporate causing separation of bitumen from water. And then bitumen spreads on the surface of the aggregate and acts as a binding material and slowly attains its strength.
Depending upon the speed at which water evaporates and bitumen particles separate from water, it is classified into following 3 types.
- Rapid Setting Emulsion (RS)
- Medium Setting Emulsion (MS)
- Slow Setting Emulsion (SS)
Note: Here the word “setting” should not mean attainment of strength; rather it means the time taken by the bitumen to separate from water.
Uses of Emulsion
| Anionic | Cationic | |||||
| RS | MS | SS | RS | MS | SS | |
| Plant Mixes | ||||||
| Open-graded | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Dense-graded | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Stockpile mix | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Pre-coated chips | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Mix Paving | ||||||
| Open-graded | ✔ | |||||
| Slurry | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Slurry for capeseal | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Micro surfacing | ✔ | |||||
| In-Place Mixes | ||||||
| RAP | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| Dense-graded | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Soil stabilization | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Spray Applications | ||||||
| Chipseal | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Fog seal–cement curing | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| Tack coat | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| Prime | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Dust palliative | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Mulch | ✔ | |||||
| Penetration macadam | ✔ | |||||
| Other | ||||||
| Waterproofing coatings | ✔ | |||||
| Driveway and footpath sealers | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
Specifications
| Property | Min | Max | Test Method |
| Test on Emulsions | |||
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 50 °C, SFS | – | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability test, 24-h, % | – | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Demulsibility, 35 mL, 0.8 % dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 20 | – | ASTM D6936 |
| Coating ability and water resistance: | |||
| Particle charge test | positive | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve test, % | – | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Distillation: | |||
| Oil distillate, by volume of emulsion, % | – | 3 | ASTM D6997 |
| Residue, % | 60 | – | ASTM D244 |
| Tests on residue from distillation test: | |||
| Penetration, 25°C (77°F), 100 g, 5 s | 40 | 250 | ASTM D5 |
| Ductility, 25°C (77°F), 5 cm/min, cm | 20 | – | ASTM D113 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene, % | 97.5 | – | ASTM D2042 |
| Property | Min | Max | Test Method |
| Test on Emulsions | |||
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 50 °C, SFS | – | 400 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability test, 24-h, % | – | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Demulsibility, 35 mL, 0.8 % dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate, % | 20 | – | ASTM D6936 |
| Coating ability and water resistance: | |||
| Particle charge test | Positive | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve test, % | – | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Distillation: | |||
| Oil distillate, by volume of emulsion, % | – | 3 | ASTM D6997 |
| Residue, % | 60 | – | ASTM D244 |
| Tests on residue from distillation test: | |||
| Penetration, 25°C (77°F), 100 g, 5 s | 40 | 250 | ASTM D5 |
| Ductility, 25°C (77°F), 5 cm/min, cm | 20 | – | ASTM D113 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene, % | 97.5 | – | ASTM D2042 |
| Property | Min | Max | Test Method | |
| Test on Emulsions | ||||
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 50 °C, SFS | – | 450 | ASTM D244 | |
| Storage stability test, 24-h, % | – | 1 | ASTM D6930 | |
| Coating ability and water resistance: | ||||
| Coating, dry aggregate | Good | ASTM D244 | ||
| Coating, after spraying | Fair | ASTM D244 | ||
| Coating, wet aggregate | Fair | ASTM D244 | ||
| Coating, after spraying | Fair | ASTM D244 | ||
| Particle charge test | Positive | ASTM D244 | ||
| Sieve test, % | – | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 | |
| Distillation: | ||||
| Oil distillate, by volume of emulsion, % | – | 12 | ASTM D6997 | |
| Residue, % | 65 | – | ASTM D244 | |
| Tests on residue from distillation test: | ||||
| Penetration, 25°C (77°F), 100 g, 5 s | – | 250 | ASTM D5 | |
| Ductility, 25°C (77°F), 5 cm/min, cm | 20 | – | ASTM D113 | |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene, % | 97.5 | – | ASTM D2042 | |
| Property | Min | Max | Test Method |
| Test on Emulsions | |||
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 50 °C, SFS | – | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability test, 24-h, % | – | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Particle charge test | Positive | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve test, % | – | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Cement mixing test, % | – | 3.0 | ASTM D6935 |
| Distillation: | |||
| Residue, % | 57 | – | ASTM D244 |
| Tests on residue from distillation test: | |||
| Penetration, 25°C (77°F), 100 g, 5 s | 40 | 250 | ASTM D5 |
| Ductility, 25°C (77°F), 5 cm/min, cm | 20 | – | ASTM D113 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene, % | 97.5 | – | ASTM D2042 |
| Property | Min | Max | Test Method |
| Test on Emulsions | |||
| Viscosity, Saybolt Furol at 50 °C, SFS | – | 100 | ASTM D244 |
| Storage stability test, 24-h, % | – | 1 | ASTM D6930 |
| Particle charge test | Positive | ASTM D244 | |
| Sieve test, % | – | 0.1 | ASTM D6933 |
| Cement mixing test, % | – | 3.0 | ASTM D6935 |
| Distillation: | |||
| Residue, % | 57 | – | ASTM D244 |
| Tests on residue from distillation test: | |||
| Penetration, 25°C (77°F), 100 g, 5 s | 30 | 250 | ASTM D5 |
| Ductility, 25°C (77°F), 5 cm/min, cm | 20 | – | ASTM D113 |
| Solubility in trichloroethylene, % | 97.5 | – | ASTM D2042 |
Warning: preg_match(): Compilation failed: invalid range in character class at offset 12 in /home/jbnbnrjo/public_html/wp-content/plugins/js_composer/include/classes/shortcodes/vc-basic-grid.php on line 177
